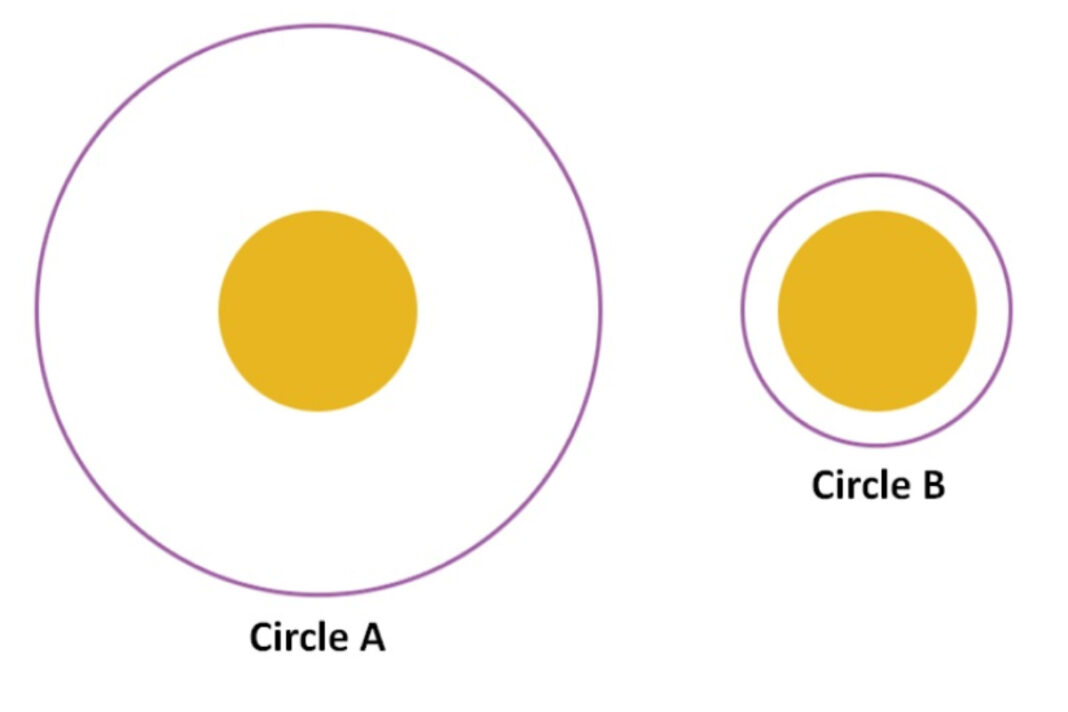
Optical Illusion: A well-known illustration of how our senses may deceive our brains is optical illusions. They serve as a reminder that we often have inaccurate perceptions of the world. There are two sets of circles in this image that is an optical illusion. While a larger circle does not encircle Circle B, it does encircle Circle A. It’s up to you to determine which circle is larger. It is really challenging to determine which circle is larger in this image. Only 1 out of 10 persons were able to provide the right response. To overcome this illusion difficulty, use ingenuity and critical thinking.
The Story Behind the Ebbinghaus Optical Illusion
Hermann Ebbinghaus published the first description of this optical illusion picture in 1892. Edward Bradford Titchener, who rediscovered the illusion in 1901, is honoured with the illusion’s name. In the solution, we go into greater detail. A contrast illusion is the name given to this kind of deception. Contrast illusions happen when the surroundings around an object causes you to perceive it as being different from what it actually is. You can put your concentration to the test by using this optical illusion. You can be more susceptible to falling for the illusion if you are not paying attention. This is due to the fact that the key to cracking this illusion problem is comparing the size of the yellow circle that is surrounded by a larger circle to the size of the yellow circle that is not surrounded by a larger circle.
DON'T MISS

Understanding the Ebbinghaus Optical Illusion
Many people must have believed that Circle B is larger, we wager. Congratulation to those who guessed correctly. In this optical illusion, the larger circle is not where you should be looking. Do not be concerned; the solution is provided below. Actually, the size of both circles is the same. The Ebbinghaus illusion, often known as the famous “Titchener circles optical illusion,” states that an object’s perceived size is affected by the size of the things around it. A central yellow circle seems smaller when it is surrounded by a larger circle in the Ebbinghaus illusion and larger when it is surrounded by a smaller circle. However, the size of the two yellow circles is identical.
Keep watching our YouTube Channel ‘DNP INDIA’. Also, please subscribe and follow us on FACEBOOK, INSTAGRAM, and TWITTER